Domestic Violence Counseling of Orlando | Life Counseling Solutions
In general domestic violence can be defined as any assault, aggravated assault, battery, aggravated battery, sexual assault, sexual battery, stalking, aggravated stalking, kidnapping, false imprisonment, or any criminal offense resulting in physical injury or death of one family or household member by another who is or was residing in the same single dwelling unit.
A “family or household member” means spouse, former spouse, persons related by blood or marriage, persons who are presently residing together as if a family, or have resided together in the past as if a family, and persons who have a child in common regardless of whether they have been married or have resided together at any time.
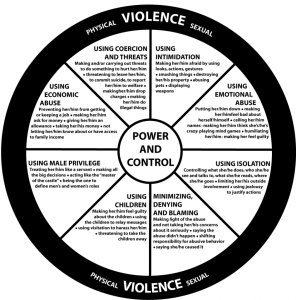
Domestic violence is not limited to physical abuse. Other tactics include emotional and psychological abuse. These three tactics are demonstrated through a Power and Control Wheel.
For example, it can be demonstrated in the following way:
Emotional and psychological abuse
The victim can exhibit:
- Anxiety disorders
- Mood disorders
- Suicide and suicidal ideation
- Somatic complaints
- Substance abuse
- Eating disorders
- High risk behaviors
- Sleep disturbance
Threats by the batterer against property, pets and other family members, and can include:
- Yelling, shouting, screaming
- Blaming
- Threats to cause harm to self or victims
- Put-downs
- Using children – to relay messages, induce guilt and to harass victim
- Play mind games
Using Privilege by:
- Treating victim like a servant
- Behaving like a “master of the castle”
- Defining male and female roles
- Destruction of belongings
- Causing economic dependence by controlling finances and assets
- Isolating the victim from any and all outside support, including family and friends
Physical domestic violence includes:
- Shooting, stabbing, pushing, grabbing, scratching, shaking, slapping, hitting, choking, kicking, biting, throwing objects.
- Stalking
- Sexual assault, sexual battery
- Reproductive control through denying access to contraceptives or forced sterilization
- False Imprisonment
- Kidnapping
- Murder
Domestic violence is an urgent public health problem with devastating consequences for women, men, children, youth and the elderly.
Domestic violence has no age, gender, social ethnic, geographic, education, economic, or race boundaries. There is no typical victim, yet it affects the health and well-being of all persons involved in the crime; in particular, contributing to children in care. As a matter of fact, the frequency and severity of violence among lower income people is equal to the frequency and severity in the middle and upper classes.
For example, according to the U.S. Department of Justice, intimate persons such as husbands, ex-husbands, boyfriends, or ex-boyfriends – commit 29 percent of all violence against women.
Further, of nearly 18 percent of American women surveyed, 17.7 million, have been raped or been a victim of attempted rape during their lifetime, according to a collaborative study on violence jointly funded by the Department of Health and Human Services and the Department of Justice.
Each year between 2 million and 4 million women are battered, and 2,000 of these battered women will die of their injuries.
Domestic violence is the single largest cause of injury to women between the ages of 15 and 44 in the United States, more than muggings, car accidents and rapes combined.
Signs of Domestic Violence
Outward physical indicators or signs are often present within a domestic violence relationship, but there are other signs in victims that reflect battering and include:
- Depression and other mental and emotional disorders.
- Difficulty maintaining employment.
- Becoming welfare recipients.
- Becoming homeless.
- Abusing children, as well as other vulnerable populations.
Other statistics include:
- Medical expenses, alone, from domestic violence range between 3 to 5 million dollars annually, but the total cost, including court, police, shelters, jail, job loss, etc…is approximately $67,000,000 annually.
- Nationally, 50 percent of all homeless women and children are on the streets because of violence in the home. (There are nearly three times as many animal shelters in the United States as there are shelters for battered women and their children.)
- Women are most likely to be murdered when attempting to leave an abusive relationship.
- In an attempt to punish the mother, there is a high risk of child abduction by the domestic violence batterer.
- 25 percent of 235 women studied reported that husbands continued to make threats against their lives during child visitations.
- 73 percent of battered women seek emergency medical care for injuries sustained after leaving their batterer.
- Approximately 2 million children in the United States are seriously abused by their parents, guardians, or others each year and approximately 20 percent of children will be sexually abused in some way, usually by someone they know- before becoming adults.
- 900,000 parents are beaten or abused by their children each year. The Elder Abuse Incidence study found that approximately 551,011 elder persons were abused or neglected in a one-year period. (1996)
- One study found that children of abused mothers were 57 times more likely to have been harmed because of intimate partner violence between their parents, compared with children of non-abused mothers.
Resources:
- American Bar Association of Domestic Violence
- Batter Intervention Services Coalition
- National Coalition against Domestic Violence http://www.ncady.org